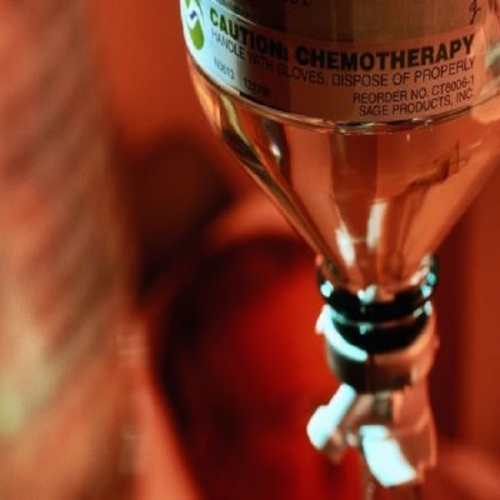
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy is the use of anticancer drugs. Moreover; it has lots of medical products to make life easier what is designed to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cancer cells in the body. It may be used:
At Cancer Treatment Centers of America® (CTCA), our medical oncologists among all medical products are experienced in delivering targeted. It individualized chemotherapy options while also proactively managing side effects.
Chemotherapy delivery methods
Some chemotherapy delivery methods include:
chemotherapy is when the chemotherapy drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cells throughout the body. When chemotherapy drugs direct to a specific area of the body, it means regional chemotherapy.
Pain management, is a branch of medicine employing an interdisciplinary approach. It uses for easing the suffering and improving the quality of life of those living with chronic pain. The typical pain management team includes medical practitioners, pharmacists, clinical psychologists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and clinical nurse specialists. The team may also include other mental health specialists and massage therapists. Pain sometimes resolves promptly once the underlying trauma or pathology has healed. Also, people can treat by one practitioner, with drugs such as analgesics and (occasionally) anxiolytics. Effective management of chronic (long-term) pain, however, frequently requires the coordinated efforts of the management team.
Medicine treats injury and pathology to support and speed healing; and treats distressing symptoms such as pain to relieve suffering during treatment and healing. When a painful injury or pathology is resistant to treatment and persists, pain persists after the injury or pathology has healed, medical science cannot identify the cause of pain, the task of medicine is to relieve suffering. Treatment approaches to chronic pain include pharmacological measures. such as analgesics, antidepressants and anticonvulsants, interventional procedures, physical therapy, physical exercise, application of ice and/or heat, and psychological measures, such as biofeedback and cognitive behavioral therapy.
General anaesthesia is medically a state of unconsciousness with loss of protective reflexes, resulting from the administration of one or more general anaesthetic agents. It allow medical procedures that would otherwise be intolerably painful for the patient; or where the nature of the procedure itself precludes the patient being awake.
A variety of medications may be administered. With the overall aim of ensuring unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, loss of reflexes of the autonomic nervous system. In some cases paralysis of skeletal muscles. Anaesthetist can typically select he optimal combination of drugs for any given patient and procedure, or another provider such as an Operating Department Practitioner, Anaesthetist Practitioner, physician assistant or nurse anaesthetist (depending on local practice), in consultation with the patient and the surgeon, dentist, or other practitioner performing the operative procedure.
Vascular surgery encompasses the diagnosis and comprehensive, longitudinal management of disorders of the arterial, venous, and lymphatic systems, exclusive of the intracranial and coronary arteries. Diplomates in vascular surgery should have significant experience with all aspects of treating patients with all types of vascular disease, including diagnosis, medical treatment, and reconstructive vascular surgical and endovascular techniques. Diplomates in vascular surgery should possess the advanced knowledge and skills to provide comprehensive care to patients with vascular disease, understand the needs of these patients, teach this information to others, provide leadership within their organizations, conduct or participate in research in vascular disorders, and demonstrate self-assessment of their outcomes.
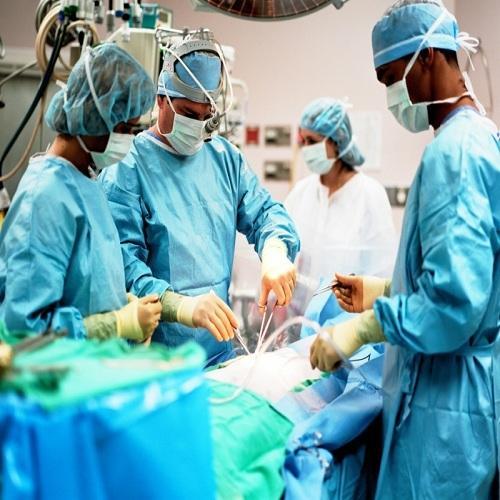
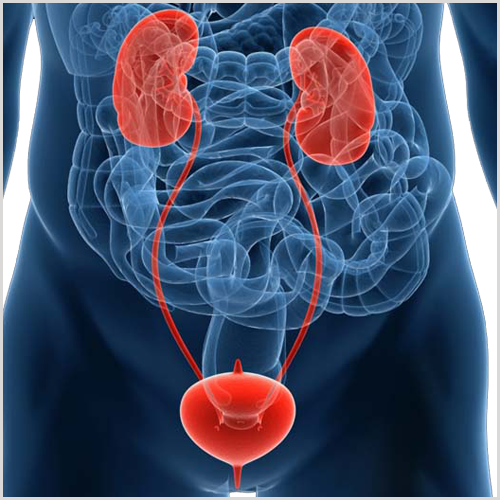
Urology also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the male and female urinary tract system and the male reproductive organs. The organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs (testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis).
The urinary and reproductive tracts are closely linked, and disorders of one often affect the other. Thus, a major spectrum of the conditions managed in urology exists under the domain of genitourinary disorders. Urology combines the management of medical (i.e., non-surgical) conditions, such as urinary tract infections and benign prostatic hyperplasia, with the management of surgical conditions such as bladder or prostate cancer, kidney stones, congenital abnormalities, traumatic injury, and stress incontinence.
Urology is traditionally on the cutting edge of surgical technology in the field of medicine, including minimally invasive roboticand laparoscopic surgery, laser-assisted surgeries, and a host of other scope-guided procedures. Urologists trained in open and minimally invasive techniques, employing real-time ultrasound guidance, fiber-optic endoscopic equipment, and various lasers in the treatment of multiple benign and malignant conditions.[1] In addition, urologists are pioneers in the use of robotics in laparoscopic surgery. Urology closely related to (and urologists often collaborate with the practitioners of) oncology, nephrology, gynaecology,andrology, pediatric surgery, colorectal surgery, gastroenterology, and endocrinology. We have needed products among all our medical products.
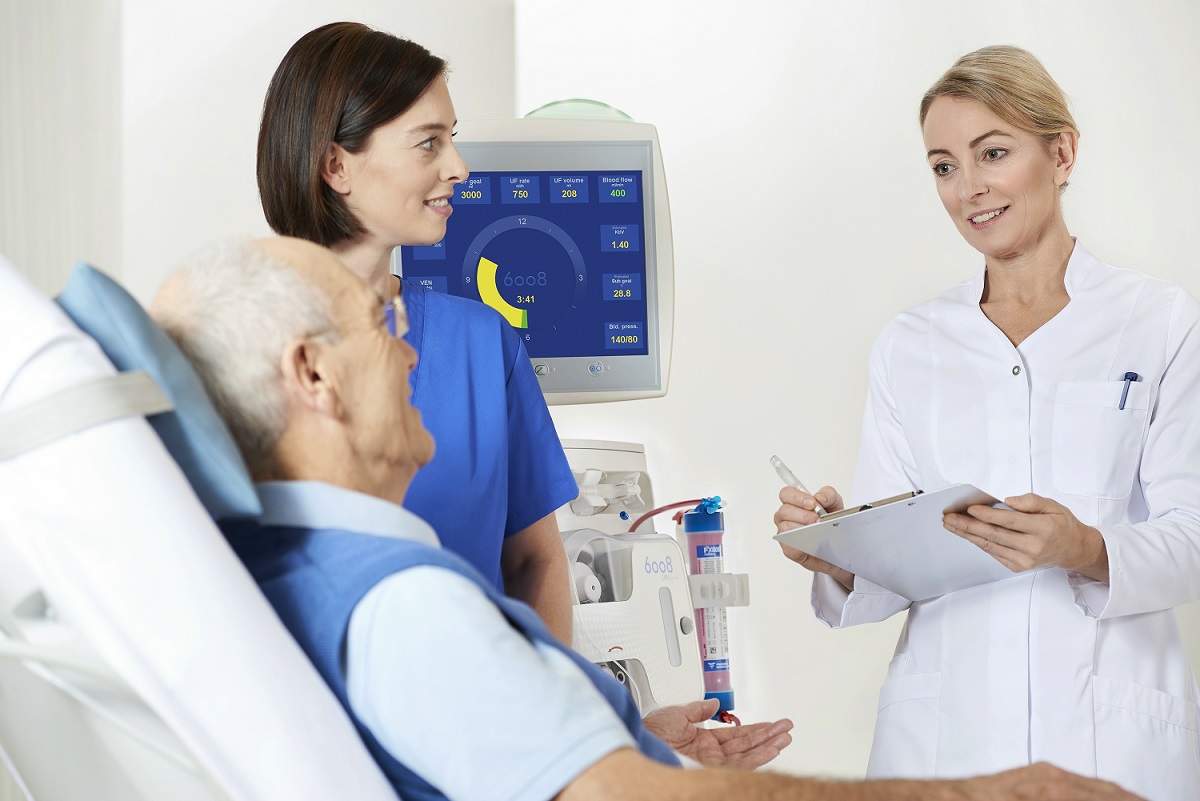
Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, commonly called kidney dialysis or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste all medical products such ascreatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies (the other two being kidney transplant and peritoneal dialysis). An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis.
Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy. Routine hemodialysis can conducte in a dialysis outpatient facility, either a purpose built room in a hospital or a dedicated, stand-alone clinic. Less frequently hemodialysis can be done at home. The specialized initiated and managed dialysis treatments in a clinic and staff made up of nurses and technicians; dialysis treatments at home can be self-initiated and managed or done jointly with the assistance of a trained helper who is usually a family member. We have the needed products among all our products.
